Refrigeration Compressors & Control Systems Catalog
Your comprehensive guide to the best compressor types and control solutions.
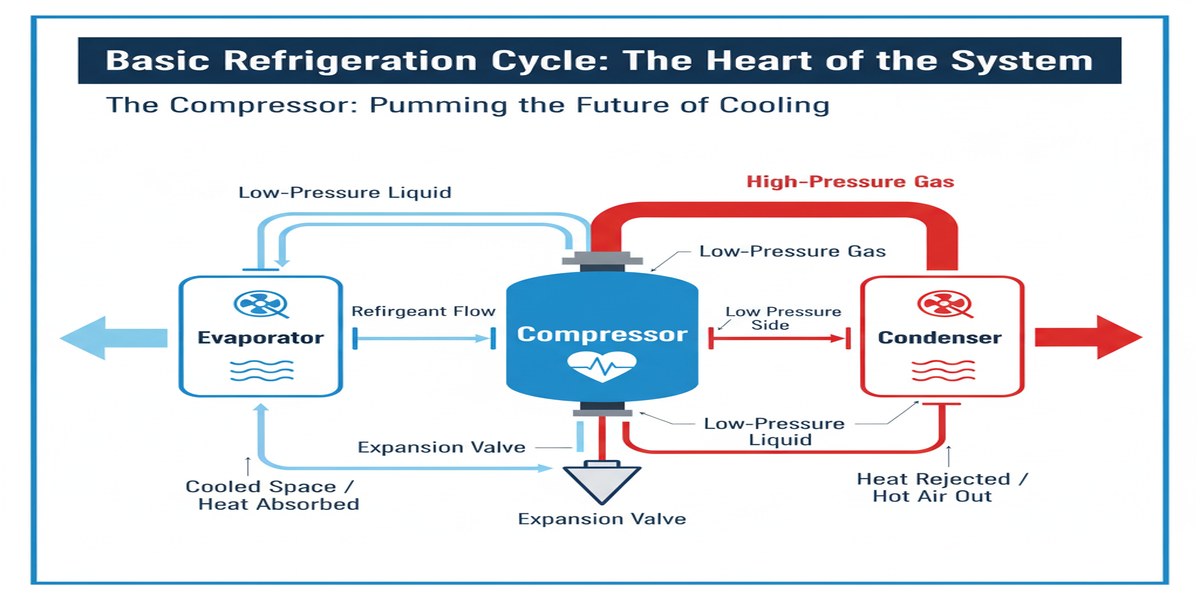
Understanding the Refrigeration Cycle
The refrigeration cycle is the fundamental process that makes cooling possible. It's a closed loop where a refrigerant fluid is circulated, compressed, and expanded to move heat from one area (like inside a cold room) to another (outside). This cycle consists of four main components: the compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator. Understanding how these parts interact is crucial for diagnosing issues and selecting the right equipment for any cooling requirement, from a simple refrigerator to a large industrial chiller.
Solutions by Application
Instead of just selling individual parts, we engineer complete, reliable, and efficient refrigeration packages. These solutions are tailored for specific commercial and industrial applications, ensuring all components work together seamlessly. Whether you need a compact system for a small cold room or a massive, parallel rack system for a supermarket, our application-based approach guarantees optimal performance, energy savings, and easier installation by providing a pre-designed and integrated package.

Cold & Freezer Rooms
Complete packages including Reciprocating Compressors, Evaporators, and Digital Controllers for precise temperature management.

Central AC (Chillers)
High-capacity solutions using Screw or Centrifugal Compressors, water-cooled condensers, and oil separators for large-scale buildings.

Supermarket Solutions
Multi-compressor rack systems managed by PLCs, using electronic expansion valves (EEVs) for maximum efficiency and reliability.
Refrigeration Compressors
The compressor is the 'heart' and the primary energy consumer in any refrigeration system. Its job is to draw in low-pressure refrigerant gas and compress it into a high-pressure, hot gas. The choice of compressor technology—whether Reciprocating, Scroll, Screw, or Centrifugal—directly dictates the system's overall energy efficiency, noise level, maintenance requirements, and operational lifespan. This section details the most common types available, helping you select the perfect match for your specific application's capacity and temperature needs.
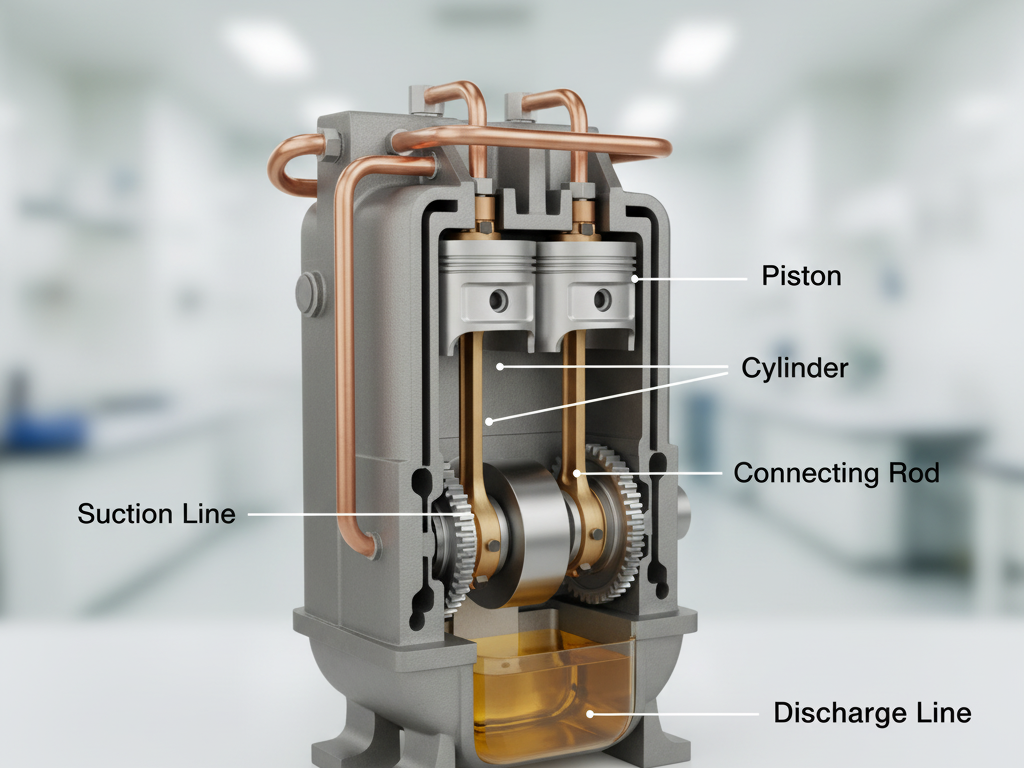
Reciprocating Compressor
Also known as the Piston Compressor, it's the most common and traditional type. It relies on the reciprocating motion of a piston inside a cylinder to compress refrigerant gas. Suitable for a wide range of small to medium applications.
- Hermetic (Sealed): Motor and compressor are sealed in one unit. Used in domestic fridges/ACs.
- Semi-Hermetic: Can be opened for on-site repairs. Used in commercial refrigeration.
- Open-Type: Compressor and motor are separate, connected by a shaft. Used in large industrial applications.
- Small cold rooms and freezers.
- Domestic refrigerators and AC units.
- Commercial display cases.
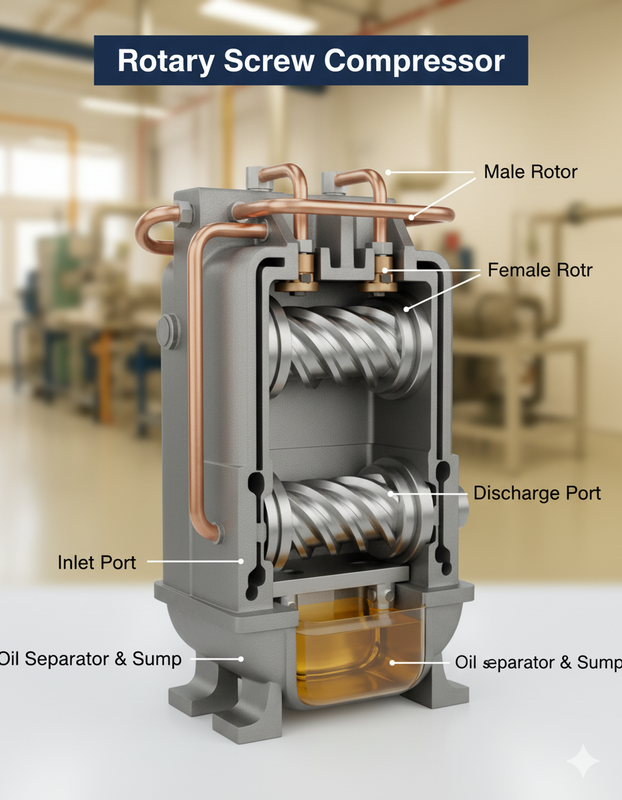
Rotary Screw Compressor
It operates via two intermeshing helical screws that rotate to compress the gas between them. Specifically designed for heavy-duty industrial applications that require continuous, round-the-clock operation with high efficiency and reliability.
- High efficiency, especially at full load.
- Durable design for continuous 24/7 operation.
- Wide capacity control range.
- Large industrial refrigeration (factories, food processing).
- Water-cooled and air-cooled chillers.
- Large supermarket rack systems.

Scroll Compressor
It uses a pair of intermeshed spiral scrolls, one fixed and one orbiting, to compress the gas. It is the most modern and efficient option for residential and light commercial air conditioning systems.
- Very high energy efficiency (EER/SEER).
- Extremely quiet operation and low vibration.
- High reliability with few moving parts.
- Residential and light commercial AC units (splits, rooftops).
- Heat pumps and VRF/VRV systems.
- Small chillers and data center cooling.
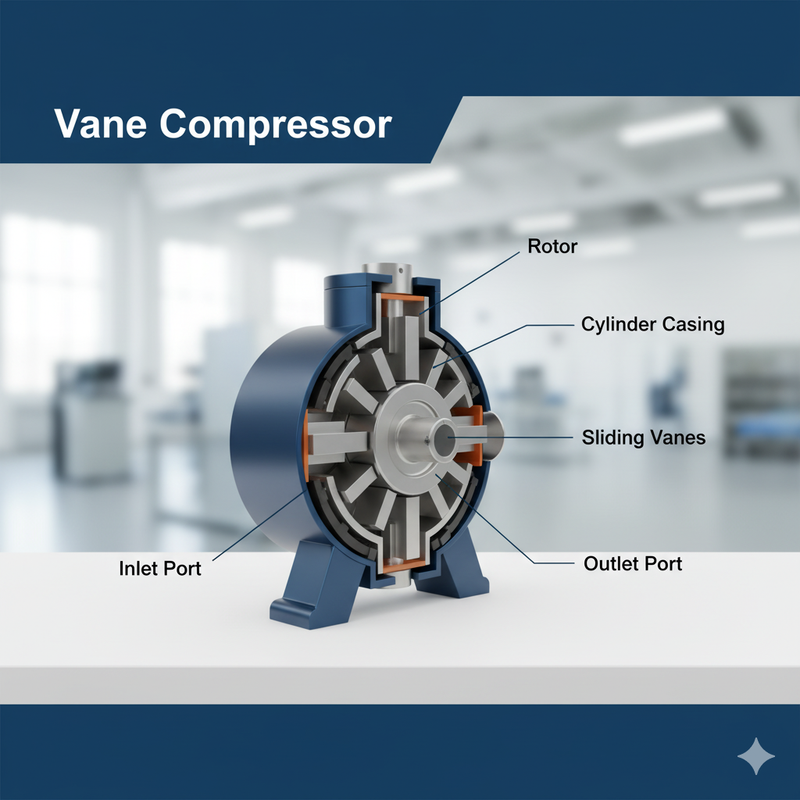
Vane Compressor
It uses a rotor with sliding vanes (blades) inside a cavity. It features a very long operational life and a simple design that provides a steady, continuous airflow, making it ideal for specific applications.
- Very long operational lifespan (often > 100,000 hours).
- Simple, compact design.
- Produces smooth, pulse-free airflow.
- Transport refrigeration (trucks, containers).
- Gas stations (air compressors).
- Industrial compressed air.

Centrifugal Compressor
Uses a high-speed rotating impeller to force gas to the outer edge, compressing it through centrifugal force. Ideal for very large capacity applications.
- Designed for very large cooling capacities (hundreds of tons).
- Oil-free operation options available (magnetic bearings).
- Excellent efficiency at high loads.
- Large water chillers for airports, malls, and hospitals.
- Industrial process cooling.
- Gas compression in refineries.

General Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance is key to extending your compressor's life and ensuring efficiency. Regular checks can prevent costly failures.
- Regularly clean condenser coils from dust.
- Check for refrigerant leaks and correct charge.
- Ensure proper voltage and check electrical connections.
- Listen for unusual noises or vibrations.
- Verify oil level and check for contamination.
- Inspect fans and belts for wear and tear.
- Monthly: Check oil levels, clean air filters, and inspect for any leaks.
- Quarterly: Tighten electrical connections, test safety controls (HP/LP switches).
- Annually: Change oil and filter driers, conduct a full system performance test.
Key Selection Criteria
Choosing the correct compressor is the most critical decision in designing a refrigeration system. A mismatch can lead to severe inefficiency, high operational costs, and premature failure. Beyond just the type of compressor, several key technical parameters must be perfectly aligned with the application's demands. These criteria ensure the system operates reliably and efficiently under its specific working conditions.
Capacity (HP / Tons)
The required cooling power for the application (e.g., small 1HP for a display case, 500-ton for a building).
Temperature Range
High (AC), Medium (Coolers), or Low (Freezers) temperature applications determine the model.
Energy Efficiency (EER/SEER)
Crucial for reducing operational costs, especially in KSA. Inverter (VFD) models offer the best efficiency.
Refrigerant Type
Must be compatible with the system refrigerant (e.g., R134a, R410A, R32, R744-CO2).
Compressor Control Systems
A control system is the 'brain' that manages the compressor and the entire refrigeration cycle. It's not just about turning the system on and off; it's about optimization, safety, and precision. Modern control systems utilize digital controllers, VFDs, and sensors to precisely manage temperatures, protect the compressor from damaging conditions (like low oil pressure or high temperatures), and significantly reduce energy consumption by matching the compressor's output to the exact cooling demand.
Pressure Switches (High/Low)
Protect the system from over-pressure (high) or loss of refrigerant (low). Essential for safety.
Digital Controllers / Thermostats
Manage the temperature of the refrigerated space by cycling the compressor on and off.
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs)
Adjusts the compressor's speed to match the cooling demand, saving significant energy (Inverter tech).
Oil Pressure Safety Control
Monitors the compressor's oil pressure to prevent mechanical failure due to poor lubrication.
Solenoid Valves
Electronically controlled valves that manage refrigerant flow to different parts of the system.
PLC for Racks
Programmable Logic Controllers used to manage multiple compressors (racks) in large supermarkets or industrial plants.
Expansion Valves (TXV/EEV)
Controls the amount of refrigerant entering the evaporator. TXV (Thermostatic) is mechanical, EEV (Electronic) is precise and efficient.
Crankcase Heaters
Prevents refrigerant from migrating and mixing with oil during off-cycles, protecting the compressor from a 'flooded start'.
Defrost Controls (Timers/Sensors)
Manages the defrost cycle (using heaters or hot gas) to remove ice build-up on freezer evaporators.
Sight Glass & Moisture Indicator
Allows visual inspection of the refrigerant charge (checking for bubbles) and detects harmful moisture in the system.
System Components & Accessories
A refrigeration system is more than just a compressor; it's an ecosystem of critical components working in harmony. This section covers the essential accessories and parts needed to build, maintain, and repair a complete and efficient system. From evaporators and condensers that handle heat exchange, to filter driers and oil separators that ensure system protection and longevity, each component plays a vital role in the refrigeration cycle's reliability.
Evaporators (Cooling Coils)
Absorb heat from the space. Available as finned coils (for air) or plate heat exchangers (for liquid).
Condensers
Release heat absorbed by the refrigerant. Types include air-cooled (most common) and water-cooled (for chillers).
Filter Driers
Critical for removing moisture, acid, and solid contaminants from the refrigerant, protecting the compressor and TXV.
Oil Separators
Capture oil discharged by the compressor (especially in screw/rack systems) and return it, ensuring proper lubrication.
Suction Line Accumulators
Prevents liquid refrigerant from entering (slugging) the compressor, which can cause catastrophic mechanical failure.
Refrigerants (Gases)
We supply common refrigerants like R134a (medium temp), R404A (low temp), R410A (AC), and new eco-friendly options like R32.
Liquid Receivers
Stores liquid refrigerant after the condenser, ensuring a solid liquid supply to the expansion valve and compensating for system charge variations.
Discharge Mufflers
Installed in the discharge line to dampen and reduce the pulsation noise created by the compressor (especially reciprocating types).
Our Featured Projects
Our expertise isn't just theoretical. We have a proven track record of successfully supplying and supporting complex refrigeration projects across Saudi Arabia. From massive industrial cold storage facilities to precision-controlled pharmaceutical plants and large-scale supermarket rollouts, our components and solutions form the backbone of reliable cooling for critical industries. These projects demonstrate our capability to handle diverse challenges and deliver results that meet the highest standards.
Large Cold Storage Warehouse
Design and installation of a 5,000 m² multi-temperature warehouse using a centralized Screw Compressor rack system.
Supermarket Chain Rollout
Supplied and commissioned PLC-controlled CO2 (R744) transcritical systems for 15 new supermarket branches.
Pharmaceutical Plant HVAC
Implementation of redundant Scroll Chiller units for process cooling and critical cleanroom air conditioning.
Our Trusted Brands
Quality and reliability are non-negotiable in refrigeration. That's why we have built strong partnerships with the world's most respected manufacturers in the industry. By supplying genuine components from these leading brands, we ensure that your system is built with parts you can trust for longevity, performance, and efficiency. Our access to this global network of suppliers means we can provide the best possible solution for your budget and technical requirements.


Contact Us for a Consultation
Via Email:
info@alsharqco.sa
Via WhatsApp: